In 2025, numerous companies are actively investing in carbon emission reduction initiatives, employing various strategies to achieve their sustainability goals.
Achieving Carbon Emission Reduction
To achieve carbon emission reduction, a combination of policy measures, technological innovations, and behavioural changes are essential. Here are the main strategies:
- Transition to Renewable Energy
- Energy Efficiency Improvements
- Electrification of Transportation
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
- Carbon Pricing
- Promoting Sustainable Agriculture and Forestry
- Circular Economy and Waste Management
- Government Policies and International Cooperation

Renewable Energy vs. Electric Energy
Renewable Energy:
- Definition: Renewable energy refers to energy sources that are naturally replenishing and virtually inexhaustible on a human timescale. These energy sources are environmentally friendly and produce minimal or no greenhouse gases.
- Examples:
- Solar Energy: Captured from the sun’s rays.
- Wind Energy: Captured from the movement of air (wind).
- Hydropower: Generated from the flow of water, often in the form of dams or river currents.
- Geothermal Energy: Heat derived from the Earth’s internal processes.
- Biomass: Energy from organic materials, such as plant and animal waste.
Electric Energy:
- Definition: Electric energy refers to energy in the form of electricity, which can be generated from a variety of sources, including both renewable and non-renewable resources.
- Examples:
- Coal-fired Power Plants: Generate electricity by burning coal.
- Natural Gas Power Plants: Generate electricity using natural gas.
- Nuclear Power Plants: Generate electricity using nuclear fission.
In essence, renewable energy is one of the key solutions to producing electric energy in a sustainable manner, which can help reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change.
How Oil is Used to Generate Electricity
Natural oil (often referred to as oil or petroleum) can be used to generate electricity, but it is less commonly used compared to other fossil fuels like coal and natural gas. When oil is used for electricity generation, it is typically burned in a thermal power plant, where the heat produced from burning the oil is used to generate steam, which in turn drives turbines connected to generators.
Why is Oil Less Common for Electricity Generation?
Cost: Oil is generally more expensive than coal and natural gas for electricity generation, especially considering the volatility in global oil prices.
Environmental Impact: Burning oil for electricity produces significant greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to air pollution and climate change. This makes it less favourable compared to cleaner energy sources, such as natural gas or renewable’s
Availability: In many regions, natural gas and coal are more readily available and more cost-effective for generating electricity.
Oil-fired power plants are used in various parts of the world, but they are typically concentrated in regions with limited access to cheaper or more abundant fuel sources like natural gas or coal. These plants are often used as backup or peaking plants to meet electricity demand during periods of high consumption. Here are some notable oil-fired power plants around the world:
Source for this list are derived from www.iea.org, https://www.eia.gov/, https://www.worldbank.org/ext/en/home, https://globalenergymonitor.org/
| Power Plant Name | Location | Fuel Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kawasaki Oil-Fired Power Plant | Kawasaki, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan | Heavy Oil (Bunker Oil) | Used for peak electricity demand and emergency power during high demand periods. |
| Yanbu Power Plant | Yanbu, Saudi Arabia | Crude Oil | Plays a significant role in Saudi Arabia’s power generation infrastructure. |
| Paiton Power Plant | Paiton, East Java, Indonesia | Oil and Coal (Dual-Fuel) | Provides electricity to meet growing demand in Indonesia, using oil when necessary. |
| Bujumbura Power Plant | Bujumbura, Burundi | Diesel Oil | Provides electricity to the capital and surrounding areas, especially during high demand. |
| Fujairah Power and Desalination Plant | Fujairah, UAE | Oil and Natural Gas | Generates electricity and desalinated water for the UAE, using oil as backup fuel. |
| Power Plant at the Azores | Azores, Portugal | Oil | Provides electricity to the islands due to limited access to alternative fuel sources. |
| Tanzania Petroleum Power Plant | Dar es Salaam, Tanzania | Diesel Oil | Provides electricity to Tanzania’s grid, using oil as the primary fuel. |
| La Planta Termoeléctrica de San Lorenzo | San Lorenzo, Santa Fe, Argentina | Oil and Natural Gas | Generates electricity using oil during fuel shortages or high demand periods. |
| Masbate Power Plant | Masbate, Philippines | Diesel Oil | Critical for local power supply, especially during peak demand. |
| Bahrain Power Plant | Manama, Bahrain | Oil | Provides electricity for Bahrain, using oil for domestic and industrial needs. |
| Malta Power Station | Marsa, Malta | Heavy Fuel Oil | One of the island’s largest energy facilities, uses oil as the primary fuel. |
| Sime Darby Power Plant | Malaysia | Oil | Supplies electricity during periods of peak demand across the country. |
| El Salvador Power Plants | Various locations, El Salvador | Diesel and Oil | Used in El Salvador during disruptions in other power sources like hydro or geothermal. |
| Puerto Rico Power Plant | Puerto Rico, USA | Oil (and Natural Gas) | Relies on oil-fired plants, especially after Hurricane Maria, to meet energy needs. |
| Jeddah Power Plant | Jeddah, Saudi Arabia | Crude Oil | Provides electricity and supports desalination in the coastal city of Jeddah. |
Primary Sources of Electricity for EVs
The source of energy for all electric vehicles (EVs) is electricity, which powers their batteries. However, the origin of this electricity can vary widely depending on how it is generated and delivered.
- Renewable Energy:
- Solar Power: Electricity generated by solar panels.
- Wind Energy: Produced by wind turbines.
- Hydropower: Sourced from dams and other water-driven systems.
- Geothermal Energy: Generated using heat from the Earth’s interior.
- Biomass Energy: Derived from organic materials.
Benefits:
- Clean and sustainable.
- Helps EVs achieve true carbon neutrality.
Challenges:
- Dependent on location and weather conditions.
- Requires infrastructure for renewable energy storage and distribution.
2. Non-Renewable Energy:
- Coal: Burned in power plants to generate electricity.
- Natural Gas: Used in gas turbines or combined cycle power plants.
- Oil: A less common source for electricity generation today.
- Nuclear Power: Generates electricity through nuclear fission.
Benefits:
- Reliable and consistent electricity supply.
- Existing infrastructure supports distribution.
Challenges:
- Higher carbon footprint for fossil fuels.
- Nuclear power poses waste disposal and safety concerns.
How EVs Use This Energy
- Charging Stations
- EVs plug into public or private charging stations connected to the grid.
- The grid electricity source determines the emissions profile of the EV.
2. On-Site Renewable Energy
- Some EV owners use home solar panels or wind turbines to charge vehicles directly.
3. Battery Technology
- EVs store energy in lithium-ion batteries or other advanced battery systems, which power the motor.
Energy Sources in Europe
The primary energy sources for electricity generation vary across European countries, reflecting their unique resource availability, historical development, and policy choices.
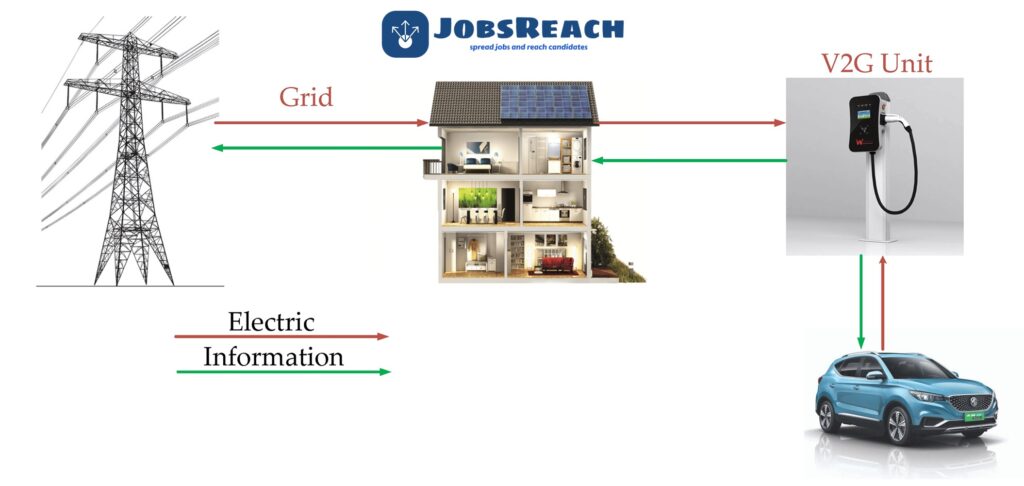
Europe’s electrical infrastructure comprises a vast network of transmission and distribution systems that deliver electricity across the continent. These grids are managed by various Transmission System Operators (TSOs) and Distribution System Operators (DSOs) to ensure a stable and efficient power supply.
Here is an updated table that includes the 40 member Transmission System Operators (TSOs) from 36 countries in Europe, as per the European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E), along with the primary energy sources for electricity generation in each country:
| Country | TSO Name | Primary Energy Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Albania | Operatori i Sistemit te Transmetimit (OST) | Hydropower |
| Austria | Austrian Power Grid AG (APG) | Hydropower, Solar, Wind |
| Belgium | Elia Transmission (Elia) | Nuclear, Natural Gas, Wind |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | BiH Independent System Operator (NOS BiH) | Coal, Hydropower |
| Bulgaria | Electroenergien Sistemen Operator (ESO) | Nuclear, Coal |
| Croatia | Croatian Transmission System Operator (HOPS) | Hydropower, Wind |
| Cyprus | Cyprus Transmission System Operator (Cyprus TSO) | Oil, Solar |
| Czech Republic | ČEPS | Coal, Nuclear, Hydropower |
| Denmark | Energinet | Wind, Biomass |
| Estonia | Elering | Oil Shale, Wind, Biomass |
| Finland | Fingrid | Nuclear, Hydropower |
| France | Réseau de Transport d’Électricité (RTE) | Nuclear, Hydropower, Wind |
| Germany | TransnetBW (TNG), TenneT, Amprion, 50Hertz | Coal, Wind, Natural Gas, Nuclear |
| Greece | Independent Power Transmission Operator (IPTO) | Natural Gas, Wind, Solar |
| Hungary | MAVIR | Nuclear, Natural Gas, Coal |
| Iceland | Landsnet | Geothermal, Hydropower |
| Ireland | EirGrid | Natural Gas, Wind, Biomass |
| Italy | Terna | Natural Gas, Solar, Wind, Hydropower |
| Latvia | Augstsprieguma tīkls (AST) | Hydropower, Wind |
| Lithuania | Litgrid | Natural Gas, Wind, Solar |
| Luxembourg | Creos Luxembourg | Imported Electricity, Natural Gas |
| Montenegro | Crnogorski elektroprenosni sistem AD (CGES) | Hydropower |
| Netherlands | TenneT | Natural Gas, Wind, Solar |
| North Macedonia | MEPSO | Coal, Hydropower |
| Norway | Statnett | Hydropower |
| Poland | Polskie Sieci Elektroenergetyczne (PSE) | Coal, Wind, Solar |
| Portugal | Redes Energéticas Nacionais (REN) | Wind, Hydropower, Solar |
| Romania | Transelectrica | Coal, Hydropower |
| Serbia | Elektromreža Srbije (EMS) | Coal, Hydropower |
| Slovakia | Slovenská elektrizačná prenosová sústava (SEPS) | Nuclear, Hydropower |
| Slovenia | Elektro-Slovenija (ELES) | Nuclear, Hydropower |
| Spain | Red Eléctrica de España (REE) | Wind, Solar, Nuclear, Hydropower |
| Sweden | Svenska Kraftnät (SVK) | Hydropower, Nuclear, Wind |
| Switzerland | Swissgrid | Hydropower, Nuclear |
| Ukraine | Ukrenergo | Coal, Nuclear, Hydro |
| United Kingdom | System Operator for Northern Ireland (SONI) | Natural Gas, Renewables (Wind, Solar) |
Primary Energy Sources
- Coal: A significant source for countries like Poland, Germany, and Serbia, but the usage is declining due to environmental concerns and EU decarbonization goals.
- Nuclear: A primary energy source for countries like France, Hungary, Slovakia, and the UK, contributing to low-carbon electricity generation.
- Hydropower: A dominant source in countries with suitable geography, such as Norway, Iceland, and Albania.
- Wind & Solar: Increasingly important in countries like Denmark, Spain, Germany, and Portugal due to the transition towards renewable energy.
- Natural Gas: Common in many countries like Italy, the Netherlands, and Greece, though it’s being gradually replaced by renewables in some regions.
Energy Sources in the United States
In the United States, the transmission of electricity is managed by a combination of Independent System Operators (ISOs) and Regional Transmission Organizations (RTOs). These entities oversee the high-voltage transmission network, ensuring reliability and efficiency in electricity delivery across various regions.

Here is a list of the primary U.S. Independent System Operators (ISOs) and Regional Transmission Organizations (RTOs), their states, and the primary energy sources they use for electricity generation:
| ISO/RTO | States Covered | Primary Energy Sources |
|---|---|---|
| California Independent System Operator (CAISO) | California | Natural Gas, Renewables (Solar, Wind), Hydropower |
| Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT) | Texas | Natural Gas, Wind, Coal |
| Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO) | 14 states: Arkansas, Iowa, Kansas, Louisiana, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, North Dakota, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Wisconsin, and parts of Canada | Coal, Natural Gas, Wind |
| ISO New England (ISO-NE) | Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, Vermont | Natural Gas, Nuclear, Renewables |
| New York Independent System Operator (NYISO) | New York | Natural Gas, Nuclear, Hydropower |
| PJM Interconnection (PJM) | 13 states: Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, New Jersey, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia | Natural Gas, Coal, Nuclear |
| Southwest Power Pool (SPP) | 14 states: Arkansas, Iowa, Kansas, Louisiana, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Texas, and Wyoming | Wind, Coal, Natural Gas |
| Alaska Systems Coordinating Council (ASCC) | Alaska | Natural Gas, Hydropower |
| Florida Reliability Coordinating Council (FRCC) | Florida | Natural Gas, Coal, Nuclear |
| Hawaii Electric Reliability Administrator (HERA) | Hawaii | Oil, Renewables (Solar, Wind), Coal |
Way forward
Renewable energy sources make EVs truly eco-friendly when used for charging.
Grid energy mix affects the environmental impact of EVs; regions with renewable-heavy grids provide cleaner electricity.
Increasing adoption of smart grids and decentralized renewable energy generation is vital to aligning EVs with global sustainability goals.
JobsReach: Bridging Talent and Resources for a Sustainable EV Future
JobsReach can contribute to EV adoption and resource identification in several ways
Connecting Talent with EV Industry: JobsReach can help match skilled professionals with companies in the electric vehicle sector, supporting the growth of EV production, research, and infrastructure development.
Promoting Green Jobs: JobsReach can highlight job opportunities in the renewable energy and EV sectors, encouraging more people to pursue careers that support sustainability and green technologies.
Supporting Resource Discovery: By linking professionals with the right networks, JobsReach can help businesses identify resources, from raw materials for EV production to innovative solutions in renewable energy and charging networks.
